DEL CLIENT AL SERVIDOR.
I DEL SERVIDOR AL CLIENT.
EL WEB SERVER
Extret de http://www.careerride.com/page/apache-http-server-620.aspx
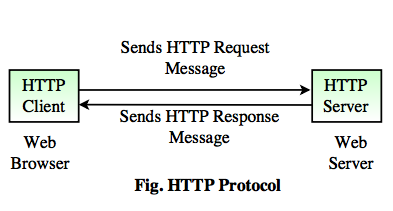
- The HTTP client (web browser) sends an HTTP request message to a running web server program and asks for a document.
- The HTTP server (web server) sends the HTTP response message to the client.
- When the client enters for the file requests by either opening a web file (typing URL in a browser’s address bar) or clicking on a hypertext link, the browser builds an HTTP request and sends it to the Internet Protocol address (IP address) indicated by the URL. The HTTP daemon in the destination server machine receives the request and sends back the requested file or files associated with the request.
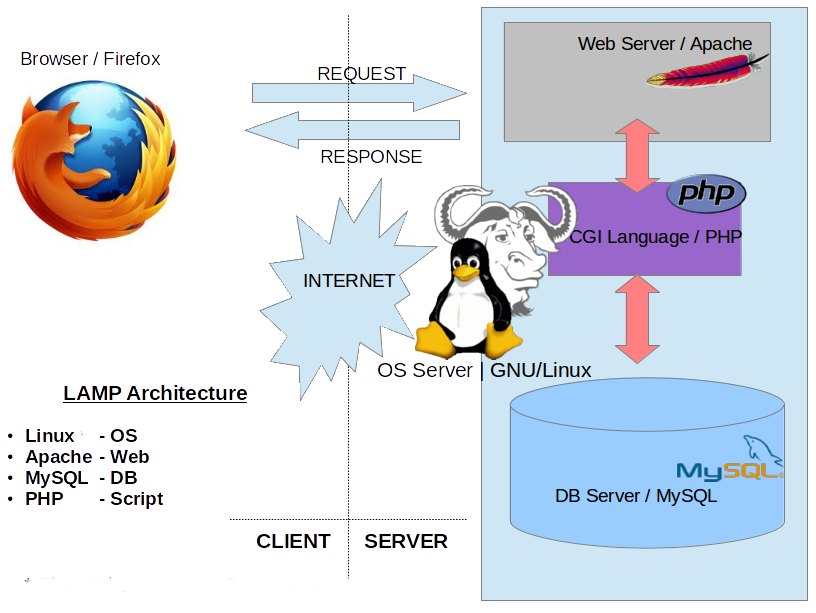
FTP: PROTOCOL DE TRANSMISSIÓ D’ARXIUS.
Explain FTP protocol.
What is FTP?
- FTP stands for File Transfer Protocol.
- It is a standard network protocol which is used to transfer computer files between a client and a server on a computer network.
- It builds on a client-server architecture.
- It uses separate control and data connections between the client and the server.
Uses of FTP Protocol:
- It is used to transfer files between a workstation and an FTP server.
- FTP servers require the user to have an account and log on to the FTP server to transfer files.
- FTP files can be transferred in both directions between server and workstation.
- It is designed to work between different systems, but it supports a limited number of file types and structures.
Modes of FTP:
There are three types of modes
1. Stream mode
2. Block mode
3. Compressed mode
1. Stream mode
It transfers files as a continuous stream from port to port with no intervention or processing of information into different formats.
2. Block mode
At this mode, FTP divides the data to be transferred into blocks of information, each with a header, byte count and data field.
3. Compressed mode
At this mode, FTP compresses the files by encoding them. These modifications of data are necessary for successful transfer because the file sender and file receiver do not have compatible data storage systems.
FTP Security:
- The need for a more secure transfer process for sensitive information such as financial data, the Netscape developed a Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) protocol in 1994.
- The SSL protocol is used to secure HTTP protocol transmissions from tampering (unauthorized user) and eavesdropping.
- Most of the industries applied this security protocol to FTP transfers, developing SFTP, a file transfer protocol armored with SSL for protection from hackers.
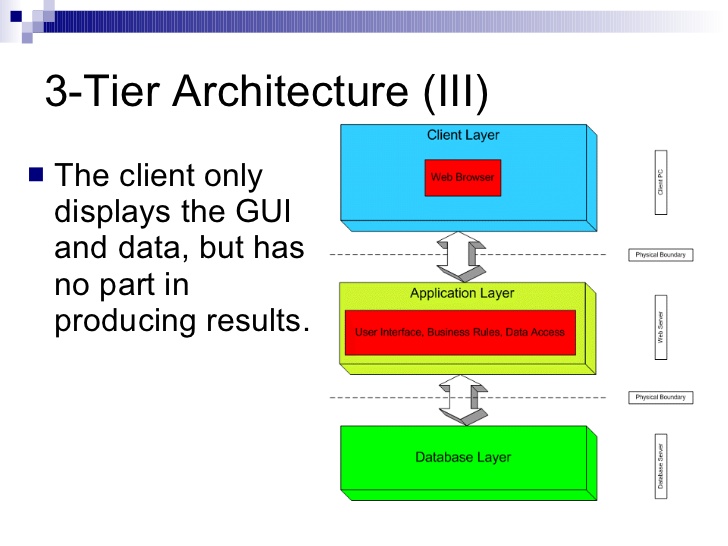
Explain the concept of 3-tier architecture with example.
What is 3-tier Architecture?
- It is a client-server architecture in which the functional process logic, data access, computer data storage and user interface are developed and maintained as independent modules on separate platforms.
- It is a software design pattern and a well-established software architecture.
- It allows any one of the three tiers to be upgraded or replaced independently.
- It is a special type of client-server architecture consisting of three well-defined and separate processes.
3-tier Architecture:
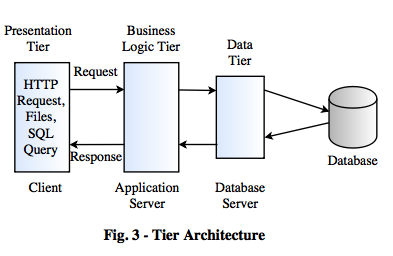
The three tiers in a 3-tier architecture are as follows:
1. Presentation Tier
2. Application Tier
3. Data Tier
- Each tier is running on a different platform.
- The user interface runs on the user’s computer (Client).
- The functional modules that actually process data. The middle tier runs on a server (Application Server).
- A Database Management System (DBMS) stores the data required by the middle tier (Database Server).
1. Presentation Tier
- It occupies the top level and displays information related to services available on a website.
- It communicates with other tiers by sending the results to the browser and other tiers in the network.
2. Application Tier
- It is also called the middle tier, logic tier, business logic.
- It controls the application functionality by performing detailed processing.
- This tier is pulled from the presentation tier.
3. Data Tier
- The information is stored and retrieved in this tier.
- The data are kept independent of application servers or business logic.
Advantages of 3-tier Architecture:
- It is easy to modify or replace one tier without affecting the other tiers.
- It separates the application functions from the database functions which makes easier to implement load balancing.
- The managing data is independent from the physical storage.
- It is possible to use different sets of developers because each tier is independent.
- The client does not have direct access to the database business logic is more secure.
- When one tier fails, there is no data loss, because it is secure by accessing the other tier.
Disadvantages of 3-tier Architecture:
- It is a more complex structure.
- It is more difficult to set up and maintain it as well.
- It is more difficult to build a 3-tier application.
- The physical separation of the tiers may affect the performance between the tree.
What is role of Middleware.
- It is a computer software which provides services to software applications from the operating system.
- It refers to the set of services composed of management systems which support the needs of a distributed, networked computing environment.
- It represents the confluence of two key areas of information technology is that, distributed systems and advanced software engineering.
Benefits of Middleware:
- It focuses on integration rather than on programming.
- It focuses on end-to-end support and integration, not just individual components.
- It increases viability of open system architectures and open-source availability.
- It helps to abstract commonly reused low-level OS concurrency and networking details into higher level.
Types of Middleware:
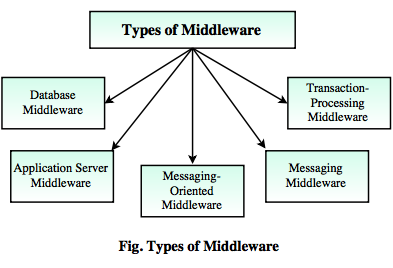
1. Database Middleware
- It enables applications to communicate with one or more local or remote database.
- This middleware does not transfer calls or objects.
- It does not allow for two-way communication between servers and clients.
2. Application Server Middleware
- It is a web-based application server.
- It provides interfaces to a wide variety of applications.
- It is used as middleware between browser and legacy systems.
3. Messaging-Oriented Middleware
- It provides an interface between client and server applications, allowing them to send data back and forth intermittently.
4. Messaging Middleware
- It is similar to an e-mail system, except that it sends data between applications.
- If the target computer is not available, the middleware stores the data in a message queue until the machine becomes available.
5. Transaction-Processing Middleware
- It is a middleware technology that sits between a requesting client program and databases.
- It ensures that all the databases are updated properly.
- The transaction-processing control program manages the transfer of data between multiple terminals and the application programs that serve them.
DINAMISME.
Describe how web server can be made dynamic.
What is a Web Page?
- It is a document available on World Wide Web.
- These document mean a web page is stored on the web server.
- The web pages can be viewed using a web browser.
- The web pages can contain huge information including text, graphics, audio, video and hyperlinks. These hyperlinks are the link to other web pages.
- The collection of web pages on a web server is known as a website. Each web page is associated with a unique URL (Uniform Resource Locator).
What is a Web Server?
- It is an information technology that processes requests via different protocols like HTTP.
- These network protocols are used to distribute information on the World Wide Web.
- It is a program that uses the HTTP protocol to perform the files from web pages to users, in response to their requests, which are forwarded by their HTTP clients (local computer).
What is a dynamic web page?
- It contains the information that changes, depending on the viewer, the time of the day, the time zone, the viewers native language and other factors.
- It can contain client-side scripting or server-side scripting to generate the changing content or a combination of both scripting types.
- It displays different content each time it viewed.
There are two types of dynamic web pages:
1. Client-Side Scripting
2. Server-Side Scripting
1. Client-Side Scripting
- In this, the web page changes in response to an action within that web page, such as a mouse or a keyboard action.
- The client-side scripts generate client-side content.
- Scripting languages such as JavaScript and Flash allow a web page to respond to client-side events.
2. Server-Side Scripting
- It is generated when a web page is loaded. For example, login pages, forums, shopping carts etc., all these are server-side scripting since those web pages change according to what is submitted to it.
- Scripting languages such as PHP, ASP, ASP.NET, JSP and Perl allow a web page to respond submission events.
How web server can be made dynamic?
-
- It is possible to change a portion of a web page by using Ajax technology.
- It shows different information at different point of time.
- It has been made possible on a web page without loading the entire web page.
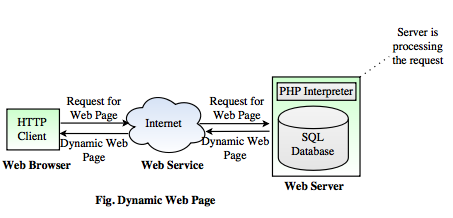
- Using HTML, scripting languages are running in the browser, a client-side dynamic web page processes the web page as it loads.
- DOM (Document Object Model) represents the loaded web page. The JavaScript and the other scripting languages determine the way the HTML in the received page is parsed into the DOM.
- In the same way, the client-side techniques can dynamically update or change the DOM. Then a dynamic web page is reloaded by the user or by a computer program to change some variable content.
- The updating information could come from the server, or from the DOM. This may or may not truncate the browsing history or create a saved version to go back.
- A dynamic web page update using Ajax technologies will neither create a page to go back, nor truncate the web browsing history forward of the displayed page.
- Using Ajax technologies the end user gets one dynamic page managed as a single page in the web browser while the actual web content rendered on that page can vary.
- The Ajax engine sits only on the browser requesting parts of its DOM, the DOM, for its client, from an application server.
What is Domain & Web hosting?
What is Domain hosting?
- It is a service that runs domain name system servers.
- Every website on the Internet needs to be hosted somewhere, so when a company hosts your website, it also hosts the domain where your site is located.
- It is optimal when the provider has multiple servers in various geographical locations that provide resilience.
- It minimizes latency for clients around the world.
What is Domain name?
- It is the identification string that defines administrative authority or control within the Internet.
- It is the name of the web site or the URL. For example, www.careerride.com
- The domain names are used in various networking contexts and application-specific naming and addressing purposes.
- It is an easy to remember address of a website. For example, it would be easy to type ‘google.com’ rather than 173.194.70.113 in the browser. But they both lead to the same web site.
- Having a domain name is not compulsory, but without it, the only person visiting the web site by using its IP address.
What is a Web Hosting?
- It is a type of Internet hosting service that allows individuals and organizations to make their web site accessible via the World Wide Web.
- It refers to the web server which stores lots of data files.
- It is a business that provides the technologies and services needed for the website or web page to be viewed on the Internet.
- Websites are hosted on a special computer called servers.
- When the user wants to view the particular website, all they need to do is type the website address into the browser. Then the user’s computer will connect to the server and the web pages will be delivered to the user through the browser.
- Many hosting company requires the domain name in order to host with the particular website. If you do not have a domain name, the hosting company helps to purchase one.
- For example, when someone types in the web address (such as www.careerride.com), the Internet connects to the web server holding that website files and then transfers that website information back to the computer. From there they can surf and view the pages of the website.
Types of Web Hosting
There are several types of Web Hosting as follows:
1. Shared Web Hosting
2. Website Builder
3. Cloud Hosting
4. Dedicated Hosting
1. Shared Web Hosting
- It is a service where one server is shared between many customers.
- It is the most common type of web hosting.
- It is easiest to start out with.
- This web hosting is cheaper and easy to use.
- It can be less flexible.
2. Website Builder
- It is the easiest way to build a website and get online.
- It provides hundreds of professionally designed templates that can be completely customized to make the website exactly the way they want.
- It is hard to customize high functionality.
3. Cloud Hosting
- It is a meeting place half way between shared hosting and dedicated hosting.
- It shares the physical server hardware with other cloud servers.
- It can be configured like a fully dedicated server.
- The website will have more resources at its disposal than shared web hosting.
4. Dedicated Hosting
- It is the meat of hosting.
- This hosting is more expensive.
- They cannot share the server resources with anyone else.
- It gives full root access to the dedicated servers.
Differentiate between static & dynamic websites.
| Sr. No. | Dynamic Website | Static Website |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | It contains information that changes. | It contains information that does not change. |
| 2. | It changes the information depending on the viewer, the time of the day, the time zone, the viewers’ native language and other factors. | It remains the same or static for every viewer of the site. |
| 3. | PHP, JavaScript is used to create dynamic pages. | HTML is used to create static pages. |
| 4. | It is more expensive to develop a website. | It is cheap to develop a website. |
| 5. | It is much easier to update a website. | It requires web development expertise to update the site. |
| 6. | The new content brings people back to the site and helps in the search engines. | The content can get static. |
| 7. | It takes a hosting cost little more. | It takes less hosting cost. |
| 8. | The dynamic website can work as a system to allow users to collaborate with the web site. | The static web site not as useful for the user. |
| 9. | It is a much more functional website. | It is not a functional website. |
| 10. | It contains the content of dynamic web pages that can be generated on-the-fly. | It contains the same prebuilt content each time the page is loaded. |
Explain in brief application of web technologies in E-commerce.
What is Web Application?
- It is a client-server software application, in which the client runs in a web browser.
- It includes more advanced applications such as project management, computer-aided design, video editing etc.
- They are popular due to the ubiquity of web browsers.
- Common web applications include webmail, online retail sales, online auctions etc.
Web Technologies for E-Commerce:
- The application requires a database store user transactions, such as the item ordered by the user.
- It also includes the middle tier – the web server and scripts executed by the server to process requests sent from the web browsers.
- A browser will send HTTP request to the middle tier, then it retrieves the information stored in the database and send a reply back to the client.
Hardware and Software:
- A web server is a hardware device which is used to host an eCommerce website.
- All the html files, databases and image files that make up the entire content of the website that are stored on the server.
- An e-Commerce can maintain the site on their own web server or pay a hosting company to provide space on a secure web server that hosts the site.
- When designing an e-Commerce solution, it is important to consider how the site is seen on the web by different browsers.
- When developing an e-Commerce site, it is important to test that the site appears in the browser window.
- A database is an integral part of an e-Commerce website. It is used to store information about the products that are for sale on the store.
- TCP is a wired connection between different machines on the Internet. A protocol is a rule of how connections are set up between two devices.
- Ports on different devices allow them to connect to other devices stored on the Internet. These ports allow a device with one IP address to access another device with a different unique IP address.
CLIENT COMUNICACIONS D’ERROR
1xx: HTTP Informational Codes
2xx: HTTP Successful Codes
3xx: HTTP Redirection Codes
307 and 308 are similar to 302 and 301, but the new request method after redirect must be the same, as on initial request.
|
4xx: HTTP Client Error Code
|
5xx: HTTP Server Error Codes
HTTP Code Comments
Wikipedia was used to produce all HTTP codes content:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/HTTP_status |
http://aula.gimnesia.net/2018/01/25/client-servidor/2on batxilleratEL WEB SERVER Extret de http://www.careerride.com/page/apache-http-server-620.aspx The HTTP client (web browser) sends an HTTP request message to a running web server program and asks for a document. The HTTP server (web server) sends the HTTP response message to the client. When the client enters for the file requests by either opening...admin pereantonibennassar@gmail.comAdministratorAula de Informàtica